Radical polymerisation for degradable polymers
One of them is radical ring-opening copolymerisation of cyclic ketene acetals (CKAs) with vinyl monomers to produce polymers with degradable ester groups in the polymer backbone.
Recently, thiocarbonyl addition-radical opening (TARO) polymerisation has a emerged as a very promising means to insert thioester degradable moities in polymer chains by copolymerising a vinyl monomer with a thionolactone. Our group developed a series of unsubstituted thionolactones of different ring sizes to prepare copolymers by TARO copolymerisation with vinyl pivalate. One of the specific features of this polymerisation is that thionolactone units coexist both in ring-opened (thioester) and ring-closed (thioketal) forms. Their relative proportion strongly depends on the ring size of the thionolactone and polymerisation conditions.
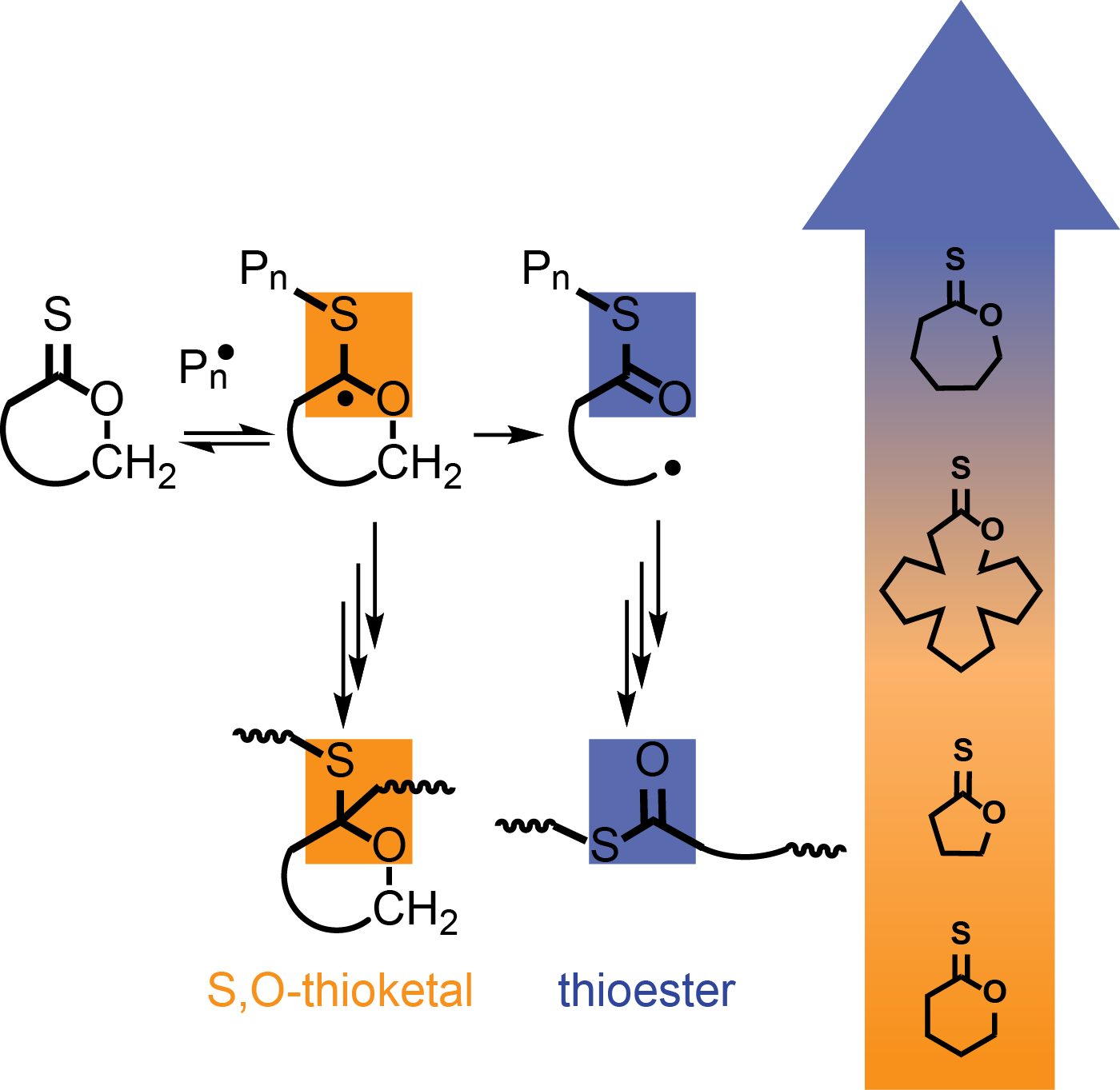
We revealed an orthogonal reactivity of thioester and thioketal links, with thioesters being selectively cleaved by aminolysis and thioketals by peroxides.
Bleach was identified as a universal agent for accelerated degradation.
More recently, we identified rac-thionolactide as a reactive comonomer for TARO copolymerization with styrene and acrylates, and to a lesser extent with MMA. Styrene-thionolactide and t-butyl acrylate-thionolactide copolymers are degraded much slower by bleach than vinyl pivalate-thionolactone counterparts
This project Holygrail is funded by ANR and Toulouse Tech Transfer, SATT Occitanie Ouest.



